Installation
- Follow the steps described in the Installation Guide.
- After the installation Bad Smells menu item should appear on Eclipse menu bar.
- In order to enable the analysis of methods belonging to library/API classes (required for Long Method bad smell) you should follow the steps shown in this guide.
- The identification of code smells can be performed on a whole Java Project, a Package Fragment Root of a project, a Package Fragment of a project, a Compilation Unit, a Type (along with its nested types), and a Method of a Type (only in the case of Long Method code smell) by selecting the appropriate element on the Package Explorer.
Feature Envy
- Open the Package Explorer View (Window -> Show View -> Package Explorer) and the Feature Envy View (Bad Smells -> Feature Envy).
- Import the Java project to be analyzed for Feature Envy bad smells and select it on the Package Explorer View.
- From the Feature Envy view click on the "Identify Bad Smells" button to run the detection process.
- In the table of the Feature Envy view you can see all refactoring opportunities identified for the selected project sorted by the value of the Entity Placement metric in ascending order.
- Each row of the table contains information about:
- the Refactoring Type of the suggestion (Move Method).
- the Source Entity (source class along with the method which is suggested to be moved).
- the Target Class.
- the value of the Entity Placement metric after the application of the corresponding refactoring.
- There is an additional row that shows the value of the Entity Placement metric of the current system.
- Double-clicking a row of the table will open both target and source classes in separate editors of Eclipse. The method to be moved will be highlighted.
- In case there is a dependency between two refactoring suggestions, a tooltip indicates which refactoring should be applied first by hovering over the dependent suggestion.
- To apply a refactoring select a row from the table and click on the "Apply Refactoring" button.
- The refactoring wizard allows to change the default name of the method suggested to be moved to the target class. The validity of the new name is automatically checked.
- After applying or undoing the application of refactoring, you have to press the "Identify Bad Smells" button again to refresh the table.
Type Checking
- Open the Package Explorer View (Window -> Show View -> Package Explorer) and the Type Checking View (Bad Smells -> Type Checking).
- Import the Java project to be analyzed for Type Checking bad smells and select it on the Package Explorer View.
- From the Type Checking view click on the "Identify Bad Smells" button to run the detection process.
- In the table of the Type Checking view you can see all refactoring opportunities identified for the selected project grouped according to their relevance.
- Each row of the table contains information about:
- the Refactoring Type of the suggestion (Replace Conditional with Polymorhism or Replace Type Code with State/Strategy).
- the Type Checking Method (the method that contains the type checking code fragment).
- the Abstract Method Name (this is the name of the polymorphic method that will be created if the corresponding refactoring is applied. The default name of the polymorphic method is the name of the type checking method).
- the number of System-Level Occurrences (this is the number of relevant suggestions corresponding to the same inheritance hierarchy at system level).
- the number of Class-Level Occurrences (this is the number of relevant suggestions corresponding to the same inheritance hierarchy at class level).
- the Average number of statements per case.
- Double-clicking a row of the table will open both the class where type checking method belongs to and the subclasses (if they exist, in case of Replace Conditional with Polymorphism refactoring) in separate editors of Eclipse.
- The code fragment that contains the type checking will be highlighted.
- The default name of the polymorphic method can be changed by clicking on the "Rename Method" button. The validity of the new name is automatically checked.
- To apply a refactoring select a row from the table and click on the "Apply Refactoring" button.
- After applying or undoing the application of refactoring, you have to press the "Identify Bad Smells" button again to refresh the table.
Long Method
In order to enable the analysis of methods belonging to library/API classes you should follow the steps shown in this guide.
- Open the Package Explorer View (Window -> Show View -> Package Explorer) and the Long Method View (Bad Smells -> Long Method).
- Import the Java project to be analyzed for Long Method bad smells and select it on the Package Explorer View.
- From the Long Method view click on the "Identify Bad Smells" button to run the detection process.
- In the tree-like table of the Long Method view you can see all refactoring opportunities identified for the selected project.
- Each leaf row of the tree-like table contains information about:
- the Refactoring Type of the suggestion (Extract Method).
- the Source Method (the method from which the slice will be extracted).
- the Variable Criterion (the variable for which the slice has been generated).
- the Block-Based Region (the region within the method body in which the slice expands).
- the ratio of Duplicated/Extracted (the percentage of the extracted slice statements that will be duplicated in both the original and the extracted methods).
- Double-clicking a leaf row of the tree-like table will open the class where source method belongs to in a separate editor of Eclipse.
- The statements belonging to the slice will be highlighted. By hovering over the highlighted statements the set of Defined and Used variables are displayed.
- To apply a refactoring select a leaf row from the tree-like table and click on the "Apply Refactoring" button.
- The refactoring wizard allows to specify the name of the method to be extracted (the default name for the extracted method is the name of the variable criterion). The validity of the new name is automatically checked.
- After applying or undoing the application of refactoring, you have to press the "Identify Bad Smells" button again to refresh the table.
God Class
- Open the Package Explorer View (Window -> Show View -> Package Explorer) and the God Class View (Bad Smells -> God Class).
- Import the Java project to be analyzed for God Class bad smells and select it on the Package Explorer View.
- From the God Class view click on the "Identify Bad Smells" button to run the detection process.
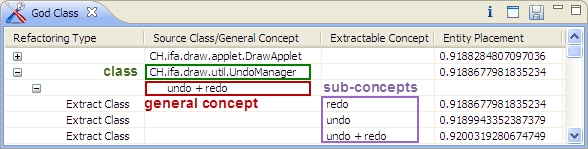
- In the tree-like table of the God Class view you can see all refactoring opportunities identified for the selected project.
- Each top-level node in the tree-like table corresponds to a class of the analyzed project. Second-level nodes represent the 'general concepts' found for the given class. The general concepts do not have any common class members.
- Each leaf row of the tree-like (third-level nodes) table contains information about:
- the Refactoring Type of the suggestion (Extract Class).
- the Source Class (the name of the class for which decompositions are suggested).
- the Extractable Concept (corresponds to a set of fields and methods from the Source class that can be extracted to a new class in order to decompose the Source class).
- the value of the Entity Placement metric after the application of the corresponding refactoring.
- Double-clicking a leaf row of the tree-like table will open the class suggested to be decomposed in a separate editor of Eclipse.
- The fields and methods which are suggested to be extracted to a new class will be highlighted.
- To apply a refactoring select a row from the table and click on the "Apply Refactoring" button. This will open a refactoring wizard that allows to specify the name of the new extracted class.
- After applying or undoing the application of refactoring, you have to press the "Identify Bad Smells" button again to refresh the table.
|
|