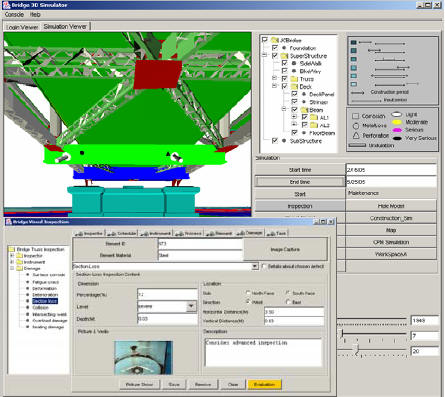
Location-based Mobile Bridge Inspection Support System
Location-Based Computing (LBC) is an
emerging discipline integrating geoinformatics, telecommunications, and
mobile computing technologies. LBC utilizes geoinformatics and tracking
methods in a distributed real-time mobile computing environment. In
LBC, elements and events involved in a specific task are registered
according to their locations in a spatial database, and the activities
supported by the mobile and wearable computers are aware of these
locations using suitable positioning devices. In this paper, we propose
a new LBC approach to support the data collection activities of bridge
inspectors (See Figure 1). The proposed prototype system is equipped
with a 3D detailed model of the bridge, and all the inspection results
are registered on the 3D model. The system navigates the inspector to
the locations he/she needs to inspect, provides information about the
results of previous inspections as augmentation of the 3D model, and
allows the inspector to add new information and to specify the location
of a new defect simply by clicking on the point of the model where the
defect has been found and then selecting the type and level of the
defect from available menus. Furthermore, the system has a rule-based
expert system that is used for data analysis and probabilistic
diagnosis based on the location and the context of the inspection tasks
in order to give the inspector suitable support. The system is
implemented in Java language and a case study about Jacques Cartier
Bridge is demonstrated.