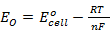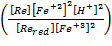Micro-Photosynthetic
Fuel Cell (μ-PSC) Modeling and Simulation
Micro-Photosynthetic
Fuel Cell (μ-PSC) generates
electrical power by continuously converting chemical energy with the
help of
the light into electrical energy through an electrochemical reaction.
In
µ-PSFC, both cell growth and cell decay occur in the anode
chamber.
During
the daytime and in the presence of light, photosynthesis takes place.
In this
stage, the electrochemical reaction in the cell utilizes carbon dioxide
and
water to produce glucose. The interaction will be reversed in both
light and
dark conditions, this process represents respiration. However in both
cases,
electrons will be released to produce electric current that passes
through the
external circuit. The produced energy is harvested with very small
scales in
order to be used for different small power rating devices.
Unconventional
renewable energy source which are scarce and
have not been explored thoroughly or exploited expansively. The photosynthetic power cell
(PSC) with micro electrical power scales is considered as one of these
resources. Although there are few prototypes fabricated earlier, there
has not
been a comprehensive electrical equivalent model developed yet.
-
To propose a mathematical model that depicts the interaction occurred in the three parts of the µ-PSC which are the anode, cathode and membrane (electrolyte) that in turn, produces electrons which are drawn outside the cell through an external load.
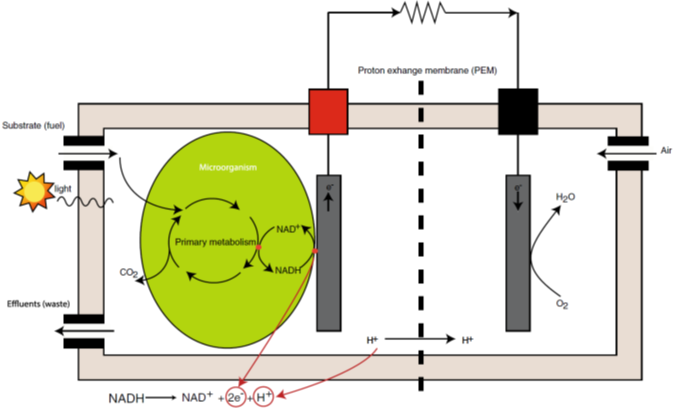
Figure (1) μ-PSC principle of operation
- To describe the principle of operation of the device that is based on photosynthesis and respiration. Both involve electron transfer chain.
|
|
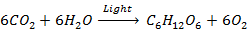 |
|
Respiration: |
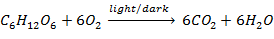 |
- To exemplify the mathematical model using electrical equivalent model which will be tested using PSIM and MATLAB/SIMULINK under different environmental conditions and electrical loads. The proposed model will then be verified experimentally using a fabricated prototype.
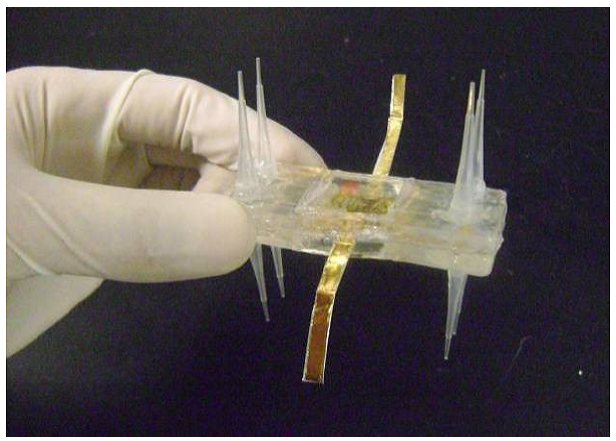
-
PSC produces energy under both dark and light conditions. So, a power electronic converter will be designed to harvest the energy and run the cell at MPP at all times. It is worth to mention that current μ-PSCs are able to report power densities of 100 - 250 mW/m2.
Simulation
Results
-
The proposed equivalent circuit for photosynthetic power cell that can be simulated and also emulated in real-time is given below:
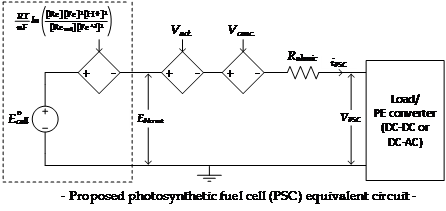
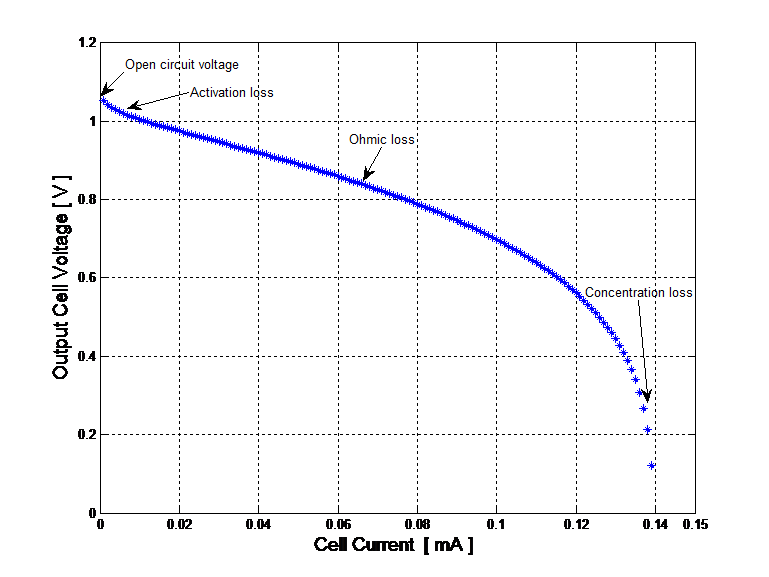
- The output characteristics of the µ-PSC is given by the V-I polarization curve.
- The output voltage of the µ-PSC is measure by using the Nernst voltage equation:
VPSC = Eo
– Vact – Vohmic – Vconc
Eo
: Open circuit
voltage (Nernst
reversible voltage)
Vact : Activation voltage loss (barrier energy)
Vohmic : Ohmic voltage
loss (electrolyte
and electrodes resistances)
Vconc : Concentration
voltage loss (transfer
resistance)
- The the electro-chemistry operation can be represented by:
|
|
|
|
E0cell
: the standard cell potential
R: the
universal gas constant
T : the
operating temperature of the cell
F : the
Faraday’s constant
- While there is a large
volume of electro-chemical research literature on, for example,
electron
transfer chains and redox processes in cell metabolism that is relevant
to
micro-photosynthetic fuel cell, relatively few studies focus
specifically on
modeling and equivalent circuit representation of μ-PSC. This is exacerbated by the fact that
on-going research continues to identify new mechanisms for electron
exchange
between growth mediums and electrodes, new design stratifies to exploit
these
and consequently new candidate organisms.
- Such organisms have not been well studied experimentally before. So, a detailed simulation and experimental study will be carried out.